Everyday Fixed Prosthodontics: Certificate Course
Everyday Fixed Prosthodontics:
Certificate Course
Course validity: 90 days
In this course you will learn:
Part 1: Material options
– Material options for indirect fixed prosthodontics
– All about PFM
– A complete guide to PFZ
– Everything you need to know about monolithic zirconia
– Can zirconia fracture
– Everything you need to know about E-max
– How are E-max restorations made
– PFM vs PFZ vs E-max for single unit posterior restorations
Part 2: Material selection
– Material selection 1: Position
– Material selection 2: Length of edentulous space
– Material selection 3: Interocclusal space
– Material selection 4: Need for bonding
– Material selection 5: Parafunctional habits
– Material selection 6: Age, allergy and laboratory competence
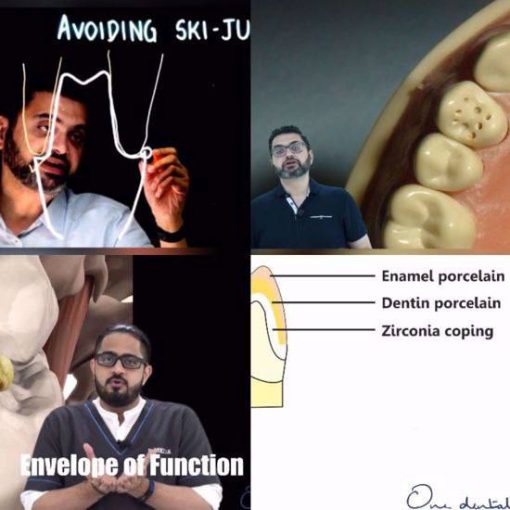
Part 3: Biologic width
– Rest In Peace biologic width!
– Understanding biologic width
– Where should I place my margins
– How to place finish lines subgingivally in a shallow sulcus
– How to place subgingival margins in a deep sulcus part 1
– How to place subgingival margins in a deep sulcus part 2
– Why is there recession or inflammation around my crown
– Diagnosing a biologic width violation
Part 4: Tooth preparation
– Principles of tooth preparation
– Detailed demonstration of tooth preparation of a molar
– Detailed demonstration of tooth preparation of a premolar
– Detailed demonstration of tooth preparation of an incisor for full ceramic crown
– Detailed demonstration of tooth preparation of an incisor for PFM crown
– Average reduction for PFM prosthesis for posterior teeth
– Average reduction for monolithic restoration for posterior teeth
– Average reduction for PFM prosthesis for anterior teeth
– Average reduction for metal free prosthesis for anterior and posterior teeth
– Tooth preparation for bridges
– Wing preparation
– Preparation of tilted, rotated and supra-erupted teeth
– Ferrule and ferrule effects
– Preaparation of intracoronal restoration
Part 5: Clearance and finish lines
– Clearance: The goal of reduction
– How can interproximal clearance be correctly achieved
– Making sense of finish lines in prosthodontics
– The importance of finish lines
– Finish line refinement
– Margin placement with respect to gingival crest
– Avoiding ski-jump ramps in finish line
Part 6: Tips and tricks in preparation
– Implications of under reduction
– Preparing the distal margin of a maxillary second molar
– The secrets to ensuring longevity of prosthesis part 1
– The secrets to ensuring longevity of prosthesis part 2
– Logic behind secondary retention and resistance features
Part 7: Tissue retraction
– Is tissue retraction really important
– Different techniques for tissue retraction
– Choosing the correct retraction cord
– What size retraction cord should I use
– Demonstration of cord packing technique
– Single cord technique
– Double cord technique
– The correct way to retrieve a cord from the sulcus
– Are there any drawbacks of retraction cords
– Cordless techniques for retraction
– Chemical haemostasis: Bleeding gums before impression making
– Techniques to achieve haemostasis prior to impression
Part 8: Impression making
– Perforated trays: A universal choice
– Metal or plastic tray for my next impression
– Triple trays for impressions
– Is buying a tray adhesive a waste of money
– Understanding impression materials and their techniques
– All about polyether
– Do automixing systems waste material
– Preparing a cartridge for light body impressions
– Bleeding a cartridge
– How to prepare putty for an impression
– Making the perfect C-Silicone impressions
– Making perfect triple tray Addition Silicone impressions
– Making one step polyether impressions
– Perfect polyether impressions using triple tray
– Disinfecting an impression
Part 9: Troubleshooting in impressions
– Troubleshooting in impressions
– Suppose my impression isn’t accurate
– Voids at the margin of my impression
– My impression tray keeps contacting teeth
– My impression separated from the tray
– My impression margins are lacking detail
– My impression keeps tearing
– Drag marks at the margin of my impression
Part 10: Pontic design
– Ideal requirements of pontics
– Natural tooth pontic
– What pontic design should I choose
– Saddle or ridge lap pontic
– Modified ridge lap pontic
– Ovate pontic
– Sanitary pontic
Part 11: Occlusion
– The basics of occlusion
– The ONE video everybody needs to watch about occlusion
– Importance of ideal occlusion
– Mutually protected occlusion
– Dynamic Occlusal Relationships
– Static occlusion for anterior teeth
– Static occlusion for posterior teeth
– Restoration of anterior guidance in anterior aesthetic case
– Canine guidance vs group function
– Types of interferences in occlusion
Part 12: Pre-cementation
– Coping trial for prosthesis
– A guide to shade selection
Part 13: Cementation
– Consequences of leaving an occlusal interference
– Cementation or bonding: A better choice
– An important tip post bonding of indirect restorations
– Sensitivity even after a root canal
– Bonding mechanism for indirect restorations
– Cementation of PFM prosthesis
– Cementaion of Emax prosthesis
– Cementation of Zirconia prosthesis
Part 14: Long lectures
– Simplified techniques of tooth preparation
– Occlusal considerations in dentistry
– The game of crowns
– Restoring endodontically treated teeth
– Articulating papers in dentistry
– Dental Ceramics
Related Products
Dental Ebook And Video
Guida alla riabilitazione implantoprotesica del mascellare posteriore atrofico pdf
Dental Ebook And Video
Oral Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, 6th edition (Original PDF from Publisher)
Dental Ebook And Video
gIDE ondemand lectures – Edentulous Patient Implant Placement and Restoration
Dental Ebook And Video
gIDE ondemand lectures – The Art and Science of Surgical Crown Lengthening
Dental Ebook And Video
Structural Analysis of Tooth – The Concept of 4 C’s by Dr. Pratiek Gupta
Dental Ebook And Video
SPEAR Using Models To Evaluate and Treatment Plan Occlusal Issues – Frank Spear
Dental Ebook And Video
B.O.P.T. сoncept encyclopedia. For prosthodontists and dental technicians
Dental Ebook And Video
Precision in Laminate Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation and Adhesive Cementation Techniques
Dental Ebook And Video
OHI-S Contemporary Advances in Implantology New Materials and Updated Protocols
Dental Ebook And Video
Tomorrow Tooth & OHI-S The 6 Elements of Orofacial Harmony – Lawrence F. Andrews
Dental Ebook And Video
OHI-S Implant-Retained Dentures Innovative Approach to Full-Arch Prosthetics
Dental Ebook And Video
RBB MasterClass,How to Succeed with Resin Bounded Bridges-Jazz Gulati
Dental Ebook And Video
Dental Ebook And Video
OHI-S Centric Relation, all Methods of Registration & Clinical Application
Dental Ebook And Video
Dental Ebook And Video
OHI-S Occlusal Compass Concept: Laboratory Protocols for Functional Rehabilitation
Dental Ebook And Video
AOX Crystal Ultra Hybrid Restoration: All Clinical & Lab Steps Start to Finish
Dental Ebook And Video
Dental Ebook And Video
Innovative Dental Marketing Ideas to Grow Your Practice – Gayle Reynolds
Dental Ebook And Video
OHi-S Biomechanics of the Mandible – Davis Thomas Accurate Diagnosis for Successful TMD Treatment
Dental Ebook And Video
Dental Ebook And Video
FMR – Full Course – Dr. Moez Khakiani (New online version with 2024 updates)
Dental Ebook And Video
OHI-S Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy Techniques in Orthodontics – Tzvika Greenbaum
Dental Ebook And Video
Dental Ebook And Video
Digital Hybrids for Dentists and Technicians Enjoy Tutorials with Exocad
Dental Ebook And Video
OTEXE A Course on Damon Ultima: Bracket System: The System’s Creator Dr.Dwight Damon
Dental Ebook And Video
Southwest Society of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons Combined Annual Meeting 2023
Dental Ebook And Video
Osteocom Implant Prosthodontics, from Planning to Restoration – David Powell